Continuo a ricevere richieste per studiare il passato prossimo con un esercizio complesso
Ho pensato di mettere insieme un quiz per aiutarvi a fare un poco di esercizio.
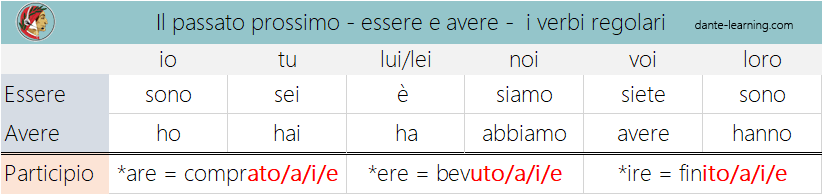
Non ci limiteremo al solito quesito “essere o avere”, che presumo già sappiate, ma aggiungeremo i verbi riflessivi, gli irregolari, i verbi modali (dovere, potere, volere, sapere) e tutto quello che uno studente di livello intermedio dovrebbe sapere.
Quiz-summary
0 of 2 questions completed
Questions:
- 1
- 2
Information
LOADING QUIZ...
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading...
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You have to finish following quiz, to start this quiz:
Results
Time has elapsed
Your score is 0 out of 0 points, (0)
| Average score |
|
| Your score |
|
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
- 1
- 2
- Answered
- Review
-
Question 1 of 2
1. Question
Passato prossimo avanzato
Quiz
Controlla il tuo punteggio e le statistiche alla fine del quiz
Scrivi la coniugazione giusta
- La mia squadra (perdere) ha perso la partita ma (noi - divertirsi) ci siamo divertiti comunque.
-
- Non appena (noi sapere) (abbiamo saputo) che eravate nei guai, (noi correre) (siamo corsi) a chiamare la polizia.
- I prezzi della carne (aumentare) (sono aumentati) ancora una volta. Per fortuna, io (smettere) (ho smesso) di mangiarla da anni.
- Quei ragazzi maleducati (saltare) (hanno saltato) la fila per salire sul treno.
- I miei due figli piccoli (prendere) (hanno preso) la varicella. Fortunatamente (guarire) (sono guariti) in poco tempo.
- Noi (maturare) (siamo maturati) molto da quando (uscire) (siamo usciti) dall'università.
- Noi (dovere) (abbiamo dovuto) cambiare la serratura delle porte per sicurezza.
- A causa della siccità, i boschi (bruciare) (sono bruciati) in pochi giorni e molte persone (dovere) (hanno dovuto) traslocare.
- Purtroppo io e mia moglie non (riuscire) (siamo riusciti) a salutarvi prima di partire. (dovere) (abbiamo dovuto) lasciare l'albergo la mattina molto presto.
- I miei genitori (mettersi) (si sono messi) in testa che vogliono una casa al mare.
- A causa di una lite tra vicini, i carabinieri (dovere) (sono dovuti) intervenire e (dovere) (hanno dovuto) arrestare due persone.
- Pensavate di poter vincere facilmente, ma (voi - doversi) (vi siete dovuti) ricredere.
Correct
- Controlla le risposte giuste e continua con la prossima domanda.
↓↓↓
Incorrect
- Controlla le risposte giuste e continua con la prossima domanda.
↓↓↓
-
Question 2 of 2
2. Question
Seleziona le frasi corrette. Potrebbe essercene più di una per gruppo.
Correct
☑ La tua selezione. Controlla il tuo punteggio finale.↓↓↓
Incorrect
☑ La tua selezione. Controlla il tuo punteggio finale.↓↓↓
Illustrazione: Leopoldo Metlicovitz – Sogno d’un valzer – 1907











 ...
...